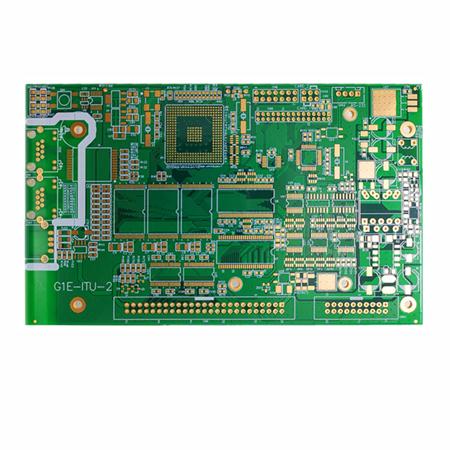
Factors Affecting Electroplating Hole Filling Process in PCB Manufacturing
The proportion of the output value of the global electroplating PCB industry in the total output value of the electronIC component industry has grown rapidly. It is the largest industry in the electronic component industry segment, and occupies a unique position. The annual output value of the electroplating PCB industry is 60 billion dollars. The volume of electronic products is becoming thinner and SMAller, and direct hole stacking on the through blind hole is a design method to obtain high-density interconnection. To do well in hole stacking, the flatness of the hole bottom should be done well first. There are several typical methods for making flat hole surfaces, and electroplating hole filling process is one of the representative ones.
Electroplating hole filling process can not only reduce the need for additional process development, but also be compatible with existing process equipment, which is conducive to obtaining good reliability.
Electroplated hole filling has the following advantages
(1) It is conducive to the design of stacked holes and disk holes (Via. on. Pad);
(2) Improve electrical performance, contribute to high frequency design;
(3) Helps to dissipate heat;
(4) Plug hole and electrical interconnection are completed in one step;
(5) The blind hole is filLED with electroplated copper, which has higher reliability and better conductivity than conductive adhesive.

ChEMIcal influencing factors
1. Inorganic chemical composition
Inorganic chemical composition includes copper (Cu:) ion, sulfuric acid and chloride.
(1) Copper sulfate. Copper sulfate is the main source of copper ions in the bath. The concentration of copper ions in the bath is kept constant through coulomb equilibrium between cathode and anode. Generally, the anode material and coating material are the same, where copper is both anode and ion source. Of course, insoluble anodes can also be used, and Cu2+is added by dissolution outside the tank, such as pure copper corner, CuO powder, CuCO, etc. However, it should be noted that the air bubbles are easily mixed with the method of adding outside the tank, which makes Cu2 in the critical state of supersaturation in the low current region and is not easy to precipitate. It should be noted that increasing the concentration of copper ions has a negative effect on the through-hole dispersion ability.
(2) Sulphuric acid. Sulfuric acid is used to enhance the conductivity of the bath. Increasing the concentration of sulfuric acid can reduce the resistance of the bath and improve the efficiency of electroplating. However, if the concentration of sulfuric acid increases in the process of hole filling electroplating, it will affect the supplement of copper ions for hole filling, which will result in poor hole filling. A low sulfuric acid concentration system is generally used in hole filling electroplating to obtain better hole filling effect.
(3) Acid copper ratio. The traditional high acid and low copper (C+: C++=8-13) system is suitable for through-hole electroplating, and the low acid and high copper (C+: Cz=3-10) plating solution system should be used for hole filling. This is because in order to obtain a good hole filling effect, the electroplating rate in the micro via should be greater than the electroplating rate on the substrate surface. In this case, compared with the traditional electroplating solution for electroplating vias, the solution formula is changed from high acid and low copper to low acid and high copper, ensuring that the supply of copper ions at the depression is free of worries.
(4) Chloride ion. The role of chloride ion is mainly to make copper ion and metal copper form a stable conversion electron transfer bridge between the electric double layers.
In the electroplating process, chloride ions can help to uniformly dissolve and etch the phOSPhor copper ball on the anode, forming a uniform anodic film on the anode surface. At the cathode, copper ions can be stably deposited by cooperating with inhibitors to reduce polarization and make the coating fine.
In addition, the conventional chlorine ion analysis is carried out in the ultraviolet visible spectrophotometer. Since the electroplating hole filling bath has strict requirements on the chloride ion concentration, and the copper sulfate bath is blue, which has a great impact on the measurement of the spectrophotometer, automatic potentiometric titration analysis should be considered.
2. Organic additives
Organic additives can refine the copper grains of the coating, improve the dispersion ability, and make the coating bright and flat. There are mainly three types of additives in acid copper plating bath: carrier, leveler and brightener.
(1) Carrier. The carrier is a polyalcohol compound of macromolecules. The carrier is adsorbed on the cathode surface and acts with chloride ions to inhibit the electroplating rate, reduce the difference between high and low current areas (i.e., increase the polarization resistance), so that copper can be uniformly and continuously deposited. At the same time, the inhibitor can act as a wetting agent to reduce the surface tension of the interface (reduce the contact angle), so that the plating solution can enter the hole more easily and increase the mass transfer effect. In hole filling electroplating, the inhibitor can also deposit copper layer uniformly.
(2) Leveling agent. The leveling agent is usually a nitrogen containing organic substance, and its main function is to adsorb in the high current density area (convex area or corner), so as to slow down the electroplating speed there, but not affect the electroplating in the low current density area (concave area), so as to level the surface. It is a necessary additive for electroplating. In general, the electroplating hole filling system with high copper and low acid will make the coating rough. Research shows that the addition of leveling agent can effectively improve the problem of poor coating.
(3) Brightener. Brighteners are usually sulfur-containing organic substances. Their main role in electroplating is to help copper ions accelerate cathodic reduction, and form new copper plating nuclei (reduce surface diffusion deposition energy), so that the copper layer structure becomes more detailed. Another function of brightener in hole filling electroplating is that if there is more brightener distribution ratio in the hole, it can help to rapidly deposit copper in the blind hole. For the hole filling electroplating of laser blind holes, all the three additives are used, and the amount of leveling agent should be properly increased, so that the leveling agent can compete with Cuz in the high current area on the plate surface, and prevent the copper from growing faster and thicker. In contrast, the recesses with more brighteners in the micro via have the opportunity to plate faster. This concept and practice is quite SIMilar to the Demasene CopperPlating in the IC copper plating process.
3. Physical influence parameters
The physical parameters to be studied include: anode type, anode cathode spacing, current density, agitation, temperature, rectifier and waveform.
(1) Anode type. When it comes to anode type, it is nothing more than soluble anode and insoluble anode. The soluble anode is usually a copper ball containing phosphorus, which is easy to produce anode mud, pollute the bath and affect the performance of the bath. Insoluble anode, also called inert anode, is generally composed of titanium mesh coated with tantalum and zirconium mixed oxide. Insoluble anode, good stability, no need for anode maintenance, no generation of anode mud, pulse or DC electroplating is applicable; However, the consumption of additives is high.
(2) Distance between cathode and anode. The spacing design between cathode and anode is very important in electroplating hole filling process, and the design of different types of equipment is also different. However, it should be pointed out that no matter how it is designed, Farad's first law should not be violated.
(3) Stir. There are many types of mixing, including mechanical swing, electrical vibration, pneumatic vibration, air mixing, and eductor. For electroplating hole filling, it is generally preferred to add jet design on the basis of traditional copper cylinder configuration. However, whether it is bottom jet or side jet, and how to arrange the jet pipe and air mixing pipe in the cylinder; What is the discharge per hour; The distance between jet pipe and cathode; If side jet is used, whether the jet is in front of or behind the anode; If the bottom jet is used, whether it will cause uneven mixing, and whether the bath stirring is weak at the top and strong at the bottom; The number, spacing and angle of the jet on the jet pipe are all factors that must be considered when designing the copper cylinder, and a lot of tests must be carried out. In addition, the most ideal way is to connect each jet pipe to the flowmeter to monitor the flow. Due to the large flow rate, the solution is easy to heat up, so temperature control is also very important.
(4) Current density and temperature. Low current density and low temperature can reduce the deposition rate of copper on the surface, while providing enough Cu2 and brightener into the hole. Under this condition, the ability of filling holes can be strengthened, but the electroplating efficiency can also be reduced.
(5) Rectifier. Rectifier is an important link in electroplating process. At present, the research on electroplating hole filling is mostly limited to full plate electroplating. If the pattern electroplating hole filling is considered, the cathode area will become very small. At this time, the output accuracy of the rectifier is required to be high.
The output accuracy of the rectifier shall be selected according to the product line and the size of the vias. The thinner the line and the smaller the hole, the higher the accuracy of the rectifier shall be required. Generally, the rectifier with output accuracy less than 5% should be selected. The high accuracy of the selected rectifier will increase the investment in equipment. For the wiring of the output cable of the rectifier, the rectifier shall be placed at the edge of the plating tank as far as possible, so as to reduce the length of the output cable and the rise time of the pulse current. The specification of rectifier output cable shall be selected to ensure that the line voltage drop of output cable is within 0.6V at 80% of the maximum output current. The required cable sectional area is usually calculated according to the current carrying capacity of 2.5A/mm. Too small sectional area of cables, too long cable length, and too large line voltage drop will cause the transmission current to fail to reach the current value required for production.
For the plating tank with the width of more than 1.6m, the method of double side incoming power shall be considered, and the length of double side cables shall be equal. In this way, the bilateral current error can be controlled within a certain range. The two sides of each flying bar of the plating tank shall be connected with a rectifier respectively, so that the current on both sides of the piece can be adjusted separately.
(6) Waveform. At present, from the waveform point of view, there are two types of electroplating hole filling: pulse electroplating and DC electroplating. Both of these methods have been studied. The traditional rectifier is used for DC electroplating hole filling, which is easy to operate, but if the plate is thick, there is nothing to do. PPR rectifier is used for pulse electroplating hole filling, which has many operation steps, but has strong processing ability for thicker plates in process.
4. Effect of base plate
The influence of substrate on electroplating hole filling can not be ignored, such as dielectric layer material, hole shape, thickness diameter ratio, chemical copper coating, etc.
(1) Medium layer material. The medium layer material has influence on the hole filling. Compared with glass fiber reinforced materials, non glass reinforced materials are easier to fill holes. It is worth noting that the glass fiber protrusions in the hole have adverse effects on chemical copper. In this case, the difficulty of electroplating hole filling is to improve the adhesion of the seed layer of the chemical coating, rather than the hole filling process itself. In fact, electroplated hole filling on glass fiber reinforced substrate has been applied in practical production.
(2) Thickness diameter ratio. At present, both manufacturers and developers attach great importance to the hole filling technology for holes of different shapes and sizes. The hole filling capacity is greatly affected by the hole thickness diameter ratio. Relatively speaking, DC systems are used more commercially. In production, the hole size range will be narrower, with a general diameter of 80pm~120Bm, a hole depth of 40Bm~8OBm, and a thickness diameter ratio of no more than 1:1.
(3) Electroless copper coating. The thickness and uniformity of electroless copper coating and the placing time after electroless copper plating all affect the hole filling performance. Chemical copper is too thin or uneven in thickness, and its hole filling effect is poor. Generally, it is recommended to fill the hole when the chemical copper thickness is>0.3pm. In addition, the oxidation of chemical copper also has a negative impact on the pore filling effect.
PCB manufacturers and PCB designers explain the factors that affect the electroplating and hole filling process in PCB manufacturing
然后
联系
电话热线
13410863085Q Q
微信

- 邮箱